NVMe vs SSD: What’s the difference?
NVMe vs SSD are both storage technologies, but they differ significantly in terms of performance, interface, and form factor. Knowing the difference between these two types of SSD is important, too, as they can have a dramatic effect on your system’s cost, size, and performance. All SSDs are faster than traditional hard drives, but there are some big differences between NVMe SSDs and SATA SSDs that are well worth considering.
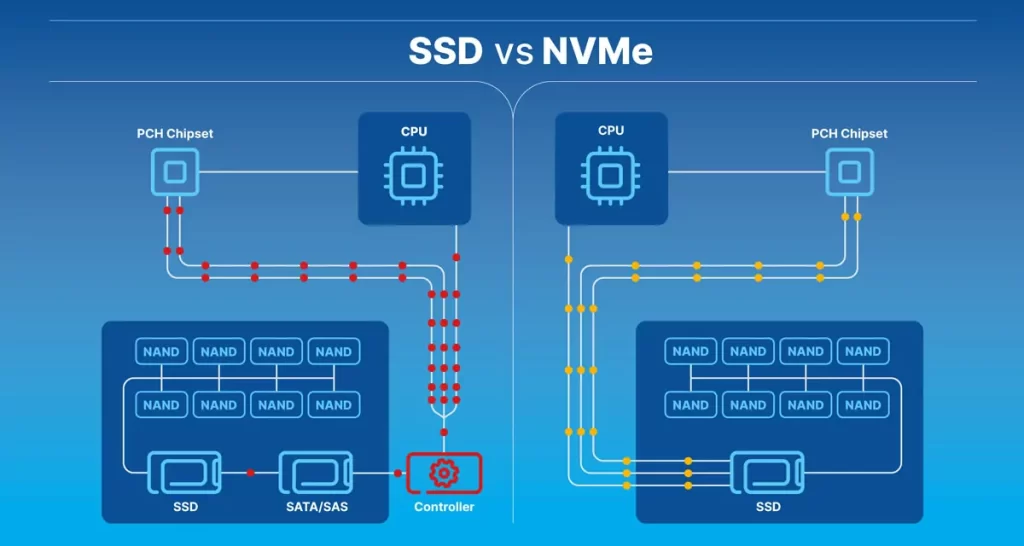
SSDs, which are based on NAND flash memory, have been around for a while and have become mainstream in consumer and enterprise computing. They connect to the system via interfaces like SATA (Serial ATA) or PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express).
NVMe, on the other hand, is a protocol designed specifically for flash storage devices, aiming to unleash the full potential of high-speed SSDs for your VPS or Dedicated servers. It utilizes the PCIe interface for communication, offering significantly faster data transfer rates compared to traditional SATA-based SSDs.
NVMe VS SSD
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) and SSD (Solid State Drive) are both storage technologies, but they differ significantly in terms of performance, interface, and form factor.
- Performance: NVMe SSDs offer significantly faster data transfer speeds compared to traditional SATA SSDs. NVMe can deliver sequential read and write speeds in excess of 3,000 MB/s, whereas SATA SSDs typically max out around 550 MB/s. This speed advantage is particularly noticeable in tasks that involve large file transfers, such as gaming, video editing, and data analysis.
- Interface: NVMe SSDs utilize the PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) interface for communication with the system, while SATA SSDs use the SATA interface. PCIe provides a higher bandwidth and lower latency compared to SATA, allowing NVMe SSDs to achieve their superior performance.
- Latency: NVMe SSDs have significantly lower latency compared to SATA SSDs. Lower latency means faster access to data, resulting in improved system responsiveness and reduced load times for applications and files.
- Form Factor: Both NVMe SSDs and SATA SSDs are available in various form factors, such as 2.5-inch drives and M.2 modules. However, NVMe SSDs are more commonly found in the M.2 form factor due to their PCIe interface. M.2 NVMe SSDs are smaller and more compact than traditional SATA SSDs, making them ideal for small form factor systems and laptops.
- Compatibility: NVMe SSDs require a motherboard with an M.2 or U.2 connector that supports the NVMe protocol. While most modern motherboards support NVMe, older systems may not be compatible. SATA SSDs, on the other hand, are compatible with a wider range of systems, as long as they have a SATA interface.
- Price: NVMe SSDs tend to be more expensive than SATA SSDs, primarily due to their faster performance and advanced technology. However, the price difference has been narrowing as NVMe becomes more mainstream.
In summary, NVMe SSDs offer superior performance compared to traditional SATA SSDs, thanks to their faster data transfer speeds, lower latency, and PCIe interface. However, whether you need an NVMe SSD depends on your specific use case and budget. For demanding workloads that require high-speed storage, such as gaming, content creation, and data analysis, NVMe SSDs can provide a significant performance boost.

Performance
When comparing the performance of NVMe vs SSDs, NVMe comes out on top in several key metrics:
- Data Transfer Speed: NVMe SSDs offer significantly higher data transfer speeds compared to SATA SSDs. NVMe SSDs can achieve sequential read and write speeds of over 3,000 MB/s, whereas SATA SSDs typically max out around 550 MB/s. This means NVMe SSDs can move data much faster, resulting in quicker file transfers and improved overall system responsiveness.
- Random Access Performance: NVMe SSDs excel in random access performance, which is crucial for tasks involving small, random read and write operations. NVMe SSDs have lower latency and higher IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second) compared to SATA SSDs, resulting in faster access to data and better performance in tasks such as loading applications, booting the operating system, and accessing frequently used files.
- Multitasking and Workloads: NVMe SSDs are better equipped to handle multitasking and heavy workloads compared to SATA SSDs. Their faster data transfer speeds and lower latency allow them to keep up with demanding tasks more effectively, making them ideal for applications such as gaming, video editing, 3D rendering, and data analysis, where rapid access to large amounts of data is essential.
- Gaming Performance: In gaming, NVMe SSDs can significantly reduce load times and improve overall gaming experience by allowing games to load assets faster. This results in shorter loading screens, smoother gameplay, and quicker level transitions compared to SATA SSDs.
- Professional Workloads: For professionals working with large datasets, such as video editors, photographers, and engineers, NVMe SSDs offer a substantial performance advantage. They can handle large file transfers, high-resolution video editing, and complex simulations with greater efficiency, leading to improved productivity and faster turnaround times.
In summary, NVMe SSDs outperform traditional SATA SSDs in terms of data transfer speed, random access performance, multitasking capability, and suitability for demanding workloads. While they may come at a higher price point, the performance benefits they offer make them a worthwhile investment for users who require fast and responsive storage solutions.
NVMe VS SSD: Key differences
The key differences between NVMe vs SSD primarily revolve around speed, interface, and form factor:
- Interface: NVMe SSDs use the PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) interface, while traditional SSDs typically use the SATA (Serial ATA) interface. PCIe offers higher bandwidth and lower latency compared to SATA, allowing NVMe SSDs to achieve faster data transfer rates.
- Speed: NVMe SSDs deliver significantly faster data transfer speeds compared to traditional SATA SSDs. NVMe can achieve sequential read and write speeds well beyond 3,000 MB/s, whereas SATA SSDs typically top out around 550 MB/s. This speed advantage is especially noticeable in tasks involving large file transfers and demanding workloads.
- Latency: NVMe SSDs have lower latency compared to SATA SSDs. Lower latency means faster access to data, resulting in improved system responsiveness and reduced load times for applications and files.
- Form Factor: Both NVMe SSDs and traditional SSDs are available in various form factors, such as 2.5-inch drives and M.2 modules. However, NVMe SSDs are more commonly found in the M.2 form factor due to their PCIe interface. M.2 NVMe SSDs are smaller and more compact than traditional SATA SSDs, making them ideal for small form factor systems and laptops.
- Compatibility: NVMe SSDs require a motherboard with an M.2 or U.2 connector that supports the NVMe protocol. While most modern motherboards support NVMe, older systems may not be compatible. SATA SSDs, on the other hand, are compatible with a wider range of systems, as long as they have a SATA interface.
- Price: NVMe SSDs tend to be more expensive than SATA SSDs, primarily due to their faster performance and advanced technology. However, the price difference has been narrowing as NVMe becomes more mainstream.
In summary, NVMe SSDs offer superior performance compared to traditional SATA SSDs, thanks to their faster data transfer speeds, lower latency, and PCIe interface. However, whether you need an NVMe SSD depends on your specific use case and budget. For demanding workloads that require high-speed storage, NVMe SSDs can provide a significant performance boost.
Conclusion
In conclusion, NVMe SSDs represent a significant advancement in storage technology compared to traditional SATA SSDs. Their key advantages include faster data transfer speeds, lower latency, and improved system responsiveness. By utilizing the PCIe interface, NVMe SSDs can achieve sequential read and write speeds well beyond 3,000 MB/s, far surpassing the capabilities of SATA SSDs.
While NVMe SSDs tend to be more expensive than SATA SSDs, the performance benefits they offer make them a compelling choice for users who require high-speed storage solutions for demanding workloads such as gaming, content creation, and data analysis. Additionally, their smaller form factor and compatibility with M.2 slots make them ideal for compact systems and laptops.
Ultimately, the choice between NVMe and SATA SSDs depends on your specific needs, budget, and system requirements. However, for users seeking the best possible performance and responsiveness from their storage devices, NVMe SSDs are undoubtedly the superior option for your Dedicated servers.